MT-Eus has three kinds of synchronization primitives,
namely mutex locks, condition variables, and semaphores.
Mutex locks are used to serialize accesses to shared variables
between threads.
Condition variables allow a thread to wait for a condition to become
true in a mutex-locked section by temporarily releasing and re-acquiring
the lock.
Semaphores are used to inform occurrences of events, or to control
sharing of finite resources.
These synchronization primitives cause voluntary context switching,
while the Solaris kernel generates involuntary task switching
on a time-sliced scheduling basis.
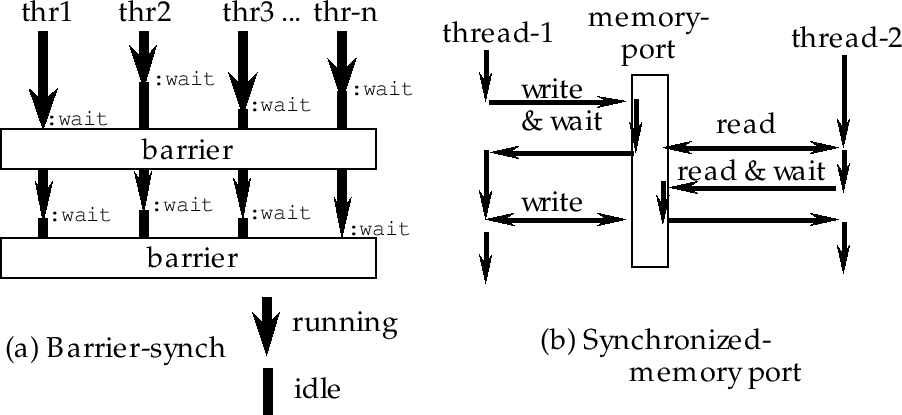
Figure 8:
Barrier synchronization and synchronozed memory port
 |
k-okada
2013-05-21